A Curated, Daily, Automated Newsletter for Tweets
January 28, 2019 | 7 min read
I decided to write a Python script that emails me a daily newsletter of a curated digest of people’s “best” tweets. This way, I can quickly catch up on the highlights from lots of people’s Twitter feeds.
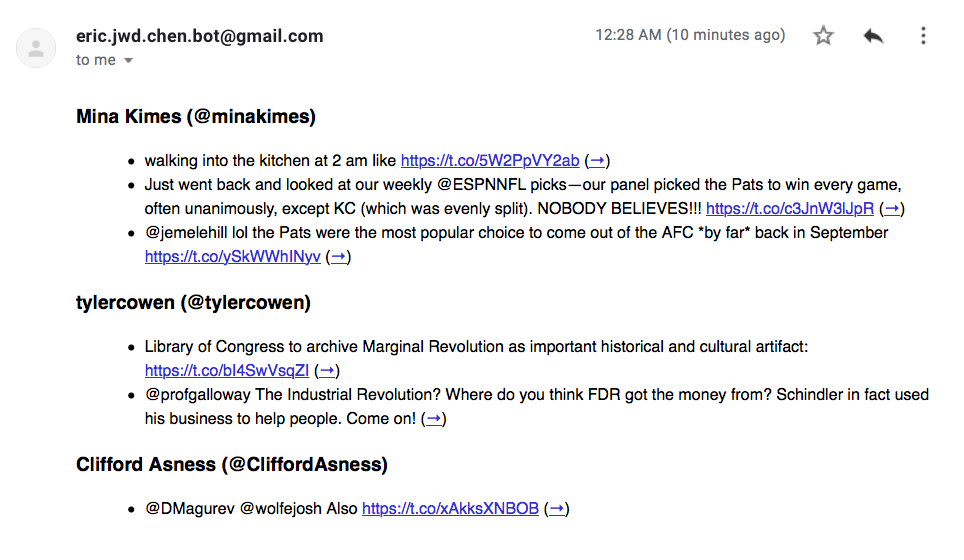 A sample of my daily newsletter of curated Tweets.
A sample of my daily newsletter of curated Tweets.
The Why
I like to keep a high signal-to-noise ratio in my Twitter feed. I follow < 50 people, and I strongly prefer people that tweet infrequently (< 5 tweets per day) and about things I find interesting almost every time.
However, there are many more people I would like to follow. Some of these people either tweet too frequently or inconsistently about things that I find interesting. Now that Twitter has an algorithmic timeline, I wish you could specify what types of content you like to see, similar how the Youtube recommended videos work. But, they don’t.
In the past, I’ve just visited these a some people’s Twitter page directly every week or so and skimmed for their most interesting content. While this keeps them out of my daily Twitter feed, I still need to sift through many tweets to find the most interesting ones. I put together this small project to fix this.
The How
I am using a couple of tools to get this job done:
-
python-twitter: a Python wrapper around the Twitter API
-
Twitter developer account: generate API keys to use in the Python script
-
Heroku: online environment for running the Python script remotely on a schedule
One key part of curation is how much to curate. First, I score all of their tweets from the past week using score = (# of favorites) * (# of retweets), e.g. 5 favorites and 10 retweets gives a score of 50. Uing the past week of data, I calculate the cutoff score for the 95th percentile. Then, of the tweets that they had in the past day, if they are above the cutoff, I include them in the daily digest email. As a final step, I have a max absolute limit for tweets I will include.
The code is below. Note, I have omitted parts of the code specific to my personal Twitter/Gmail accounts. You will need to replace those with strings for your specific accounts. You can find all of these strings by searching for 'REPLACE'.
import twitter
import numpy as np
from dateutil.parser import parse
from datetime import datetime, timezone, timedelta
def send_email(user, pwd, recipient, subject, body):
"""Sends email through Gmail based on arguments.
Based on:
https://docs.python.org/3.4/library/email-examples.html
Args:
user: A string for the Gmail address to send mail from, include @gmail.com.
pwd: A string for the Gmail account password corresponding to user.
recipient: A string or list of strings for email recipients.
subject: A string containing the email subject.
body: A string containing the email body in HTML.
Returns:
This function does not return any values.
"""
import smtplib
from email.mime import multipart, text
# parse variables to use for email
FROM = user
TO = recipient if isinstance(recipient, list) else [recipient]
SUBJECT = subject
TEXT = body
# Create message container - the correct MIME type is multipart/alternative.
msg = multipart.MIMEMultipart('alternative')
msg['Subject'] = SUBJECT
msg['From'] = FROM
msg['To'] = ", ".join(TO)
msg.attach(text.MIMEText(TEXT, 'html')) # Attach part into message container.
try:
server = smtplib.SMTP("smtp.gmail.com", 587)
server.ehlo()
server.starttls()
server.login(user, pwd)
server.sendmail(FROM, TO, msg.as_string())
server.close()
print('👍 successfully sent the mail')
except:
print("failed to send mail")
def get_tweets(api, screen_name, max_time_days=1):
"""Get recent tweets from user in timeframe.
Based on:
https://github.com/bear/python-twitter/blob/master/examples/get_all_user_tweets.py
Args:
api: An authenticated python-twitter API object.
screen_name: A string for the twitter user to get tweets from.
max_time_days: An integer for how many days of tweets to retrieve.
Returns:
A list of recent tweets from the user in the given timeframe.
"""
fetch_size = 25
timeline = api.GetUserTimeline(screen_name=screen_name, count=fetch_size)
earliest_tweet = min(timeline, key=lambda x: x.id).id
earliest_tweet_date = parse(min(timeline, key=lambda x: x.created_at).created_at)
current_date = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
max_time_delta = timedelta(days=max_time_days)
while max_time_delta > current_date - earliest_tweet_date:
tweets = api.GetUserTimeline(screen_name=screen_name,
max_id=earliest_tweet - 1, count=fetch_size)
new_earliest = min(tweets, key=lambda x: x.id).id
earliest_tweet_date = parse(
min(tweets, key=lambda x: x.created_at).created_at)
if not tweets or new_earliest == earliest_tweet:
break
else:
earliest_tweet = new_earliest
timeline += tweets
timeline_filtered = [tweet for tweet in timeline if current_date -
parse(tweet.created_at) < max_time_delta]
return timeline_filtered
def score_tweet(tweet):
"""Generate a significance score for a tweet
Formula for scoring a tweet: (# favorites) * (# retweets)
Args:
tweet: A tweet to score.
Returns:
Integer for this tweet's score.
"""
return(tweet.favorite_count * tweet.retweet_count)
def curate_tweets(api, screen_name, curate_percentile=95, curate_days=1,
curate_max=3, baseline_days=7):
"""Curate recent best tweets from a user.
Args:
api: A list of tweets to convert to HTML.
screen_name: A String of user whose timeline to curate from.
curate_percentile: Integer for percentile to use as cutoff for curating tweets.
Only include tweets that score at or above the percentile.
curate_days: Integer for how many days to curate from.
curate_max: Integer for maximum number of tweets to return. If more tweets
reach the curate_percentile cutoff than curate_max, then include only the
highest scoring tweets.
baseline_days: Integer for how many days to form baseline score for this
user's tweets. This baseline is used to calculate the cutoff score that
corresponds to curate_percentile.
Returns:
A list of curated Tweets for specified screen_name user. Sorted in
descending order based on score.
"""
# establish a baseline for twitter engagement
historical_tweets = get_tweets(api, screen_name, max_time_days=baseline_days)
list_scores = [score_tweet(tweet) for tweet in historical_tweets]
cutoff_score = min(np.percentile(list_scores, curate_percentile), 1)
# filter the timeline
tweets_digest = get_tweets(api, screen_name, max_time_days=curate_days)
tweets_filter = [tweet for tweet in tweets_digest
if score_tweet(tweet) >= cutoff_score]
tweets_sort = sorted(tweets_filter,
key=lambda x: score_tweet(x), reverse=True)
# if there are more tweets than curate_max, return only the highest scoring
return(tweets_sort[:curate_max])
def clean_string(raw_string):
"""Remove line breaks from a string
Args:
raw_string: A string to clean.
Returns:
A cleaned version of the string without line breaks.
"""
return(
raw_string.
replace('\n', ' ').
replace('\r', '')
)
def strings_to_html(list_strings):
"""Converts a list of strings to an unordered HTML list
Args:
list_strings: A list of strings to turn into an HTML list of those strings.
Returns:
An unordered HTML list of list_strings.
"""
html = '<ul><li>' + '</li><li>'.join(list_strings) + '</li></ul>'
return(html)
def tweet_to_html(tweet):
"""Convert tweet object to string representation in HTML.
Args:
tweet: A tweet to convert to HTML.
Returns:
A string that is an HTML format for representing the tweet.
"""
tweet_text = clean_string(tweet.full_text)
tweet_url = 'https://twitter.com/i/web/status/' + tweet.id_str
# ' ' is a double space in html
return('%s (<a href="%s">→</a>)' % (tweet_text, tweet_url))
def get_email_subject():
"""Generate email subject based on current date.
Returns:
A string for the email subject.
"""
string_curr_date = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%B %d, %Y')
return('Twitter digest for ' + string_curr_date)
def tweets_to_html(tweets):
"""Produce an html representation for a list of tweets.
Args:
tweets: A list of tweets to convert to HTML.
Returns:
A cleaned version of the string without line breaks.
"""
if len(tweets) == 0:
return('')
else:
user = tweets[0].user
html = '<h3>%s (@%s)</h3>' % (user.name, user.screen_name)
list_html_tweets = [tweet_to_html(tweet) for tweet in tweets]
html += strings_to_html(list_html_tweets)
return(html)
def get_name(api, screen_name):
"""Get the name associated with a Twitter screen_name.
Args:
api: An instance of authenticated Twitter API
screen_name: A string for twitter username to find name of
Returns:
String which is the name for given Twitter screen_name.
"""
user = api.GetUser(screen_name=screen_name)
return(user.name)
def main():
# Twitter API authentication
CONSUMER_KEY = 'REPLACE'
CONSUMER_SECRET = 'REPLACE'
ACCESS_TOKEN = 'REPLACE'
ACCESS_TOKEN_SECRET = 'REPLACE'
api = twitter.Api(consumer_key=CONSUMER_KEY,
consumer_secret=CONSUMER_SECRET,
access_token_key=ACCESS_TOKEN,
access_token_secret=ACCESS_TOKEN_SECRET,
tweet_mode='extended',
sleep_on_rate_limit=True)
# list of screen names to curate from, sort by Twitter name
list_screen_names = sorted([
'REPLACE',
'REPLACE',
], key=lambda x: get_name(api, x).lower())
# send email
FROM_GMAIL = 'REPLACE'
GMAIL_PASSWORD = 'REPLACE'
TO_EMAIL = 'REPLACE'
subject = get_email_subject()
text = ''
for screen_name in list_screen_names:
timeline_curate = curate_tweets(api=api, screen_name=screen_name)
text = ''.join([text, tweets_to_html(timeline_curate)])
send_email(FROM_GMAIL, GMAIL_PASSWORD, TO_EMAIL, subject, text)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()